Xanthelasma
What is xanthelasma?
Xanthelasma is a skin condition that presents with yellow patches or plaques around the eyes. They are caused by deposits of cells filled with cholesterol within the skin. Though getting xanthelasma warrants getting some bloodwork to check on cholesterol, most patients with xanthelasma will have normal cholesterol in the blood. The reason for this condition is not fully understood, and even medications that reduce cholesterol do not appear to change the appearance of xanthelasma.
What treatments are available for this condition?
Xanthelasma can be treated – but it can also come back. When patients want to avoid traditional surgery, we consider doing a series of chemical peel treatments or using an ablative laser.
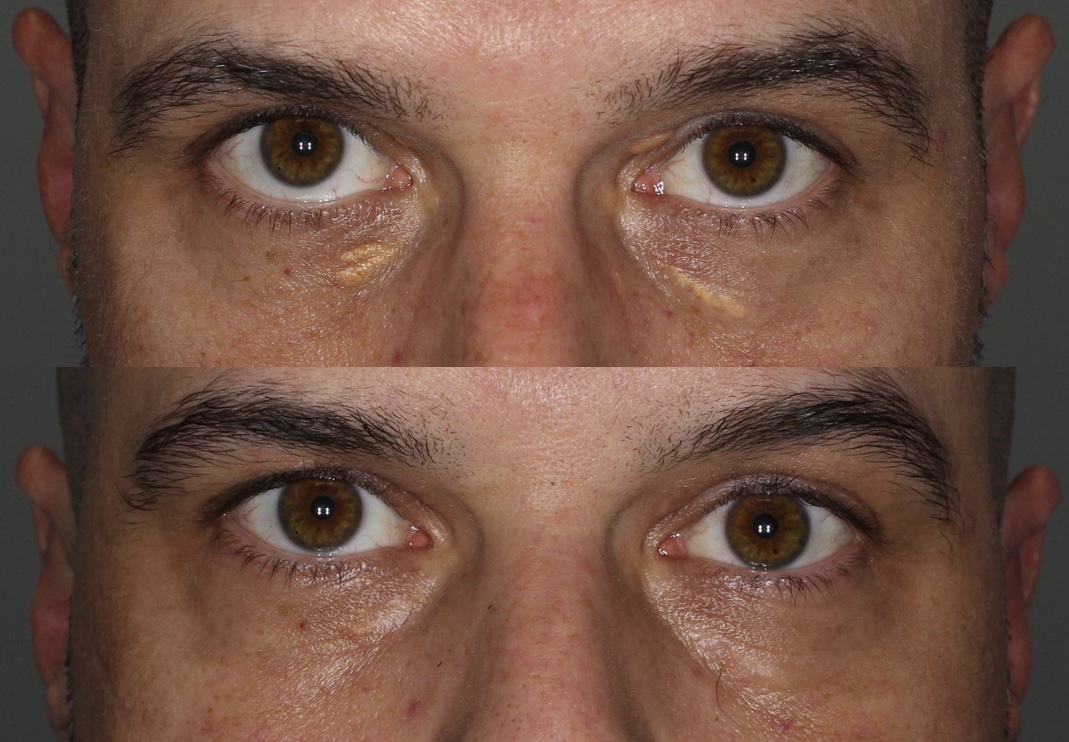
Trichloroacetic (TCA) acid is a chemical peel agent can be applied to the skin – the acid breaks down the cholesterol in the xanthelasma. There is stinging during the procedure, and for a few minutes the skin is turned ivory white (“frosting”) before healing with a crust/blister. Depending on the thickness and size of xanthelasma, two to four treatments are often required.
An ablative laser is a high-energy laser light that can vaporize precise layers of skin. When treating the skin close to the eyes, a metal contact lens (corneal shield) is placed before the procedure to protect the eye. Once the skin is cleansed and local anesthetic injected, the xanthelasma is vaporized layer by layer.
